Managing audio input devices is crucial for ensuring clear communication during video calls, recording high-quality audio, and streaming content on Windows 11. Whether you’re using a built-in microphone, USB headset, XLR interface, or professional condenser mic, properly configuring your input devices can dramatically improve your audio quality. This comprehensive guide focuses exclusively on Windows 11 systems and covers everything from basic microphone selection to advanced input management techniques that will help you achieve professional-grade audio capture.
Understanding Audio Input Devices in Windows 11
Audio input devices capture sound and convert it into digital signals. Windows 11 supports many input types — from built-in laptop mics and webcam microphones to USB mics, headsets, and professional audio interfaces.
While multiple devices can be connected at once, only one can serve as the default recording device at a time. Windows 11 assigns each device a specific role, though individual apps may override system defaults with their own preferences. Recent Windows 11 updates have improved device detection, visual feedback, and automated troubleshooting for common microphone issues.
Watch This Tutorial: How To Change And Manage Default Sound Input Device in Windows 11
Accessing Audio Input Settings in Windows 11
Windows 11 provides streamlined access to input device management through the redesigned Settings app. Follow these steps to access your audio input settings:
Step 1: Right-click the speaker icon in the system tray located at the bottom-right corner of your screen.
Step 2: Select “Sound settings” from the context menu, or alternatively navigate to Settings > System > Sound.
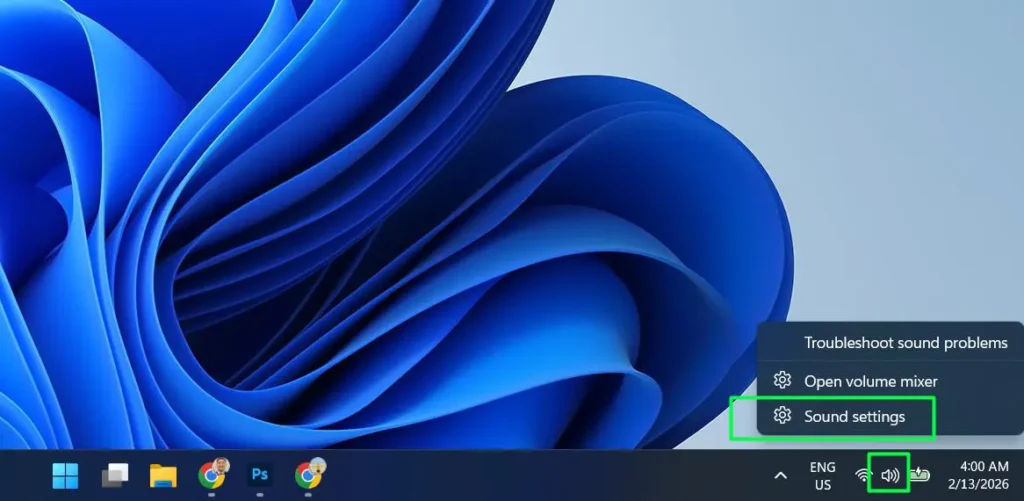
Step 3: Scroll down to the Input section where you’ll find “Choose a device for speaking or recording” along with a list of all available microphones and input devices.
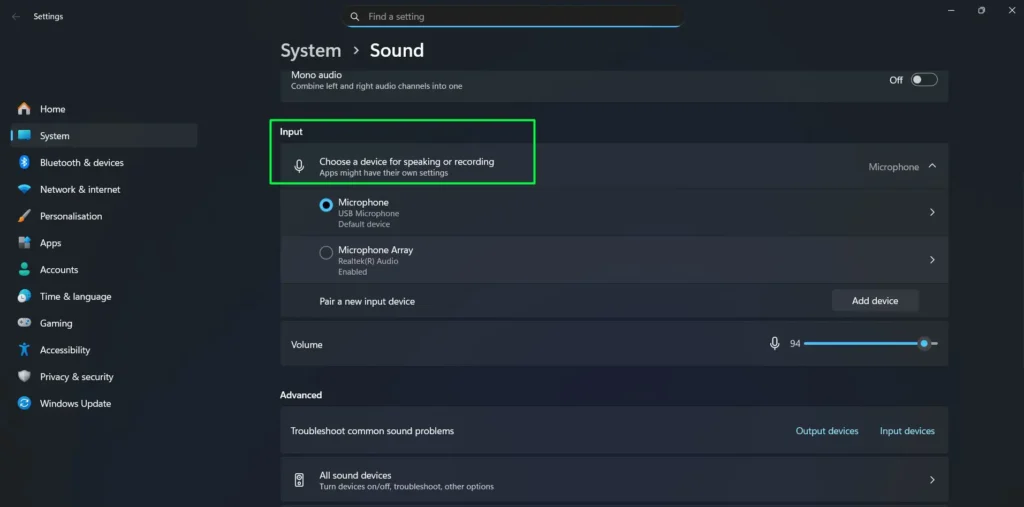
Step 4: Click on your preferred input device to select it as your default. Windows 11 displays the device name along with its connection type, making it easy to identify which microphone you’re selecting.
Below the device selection, you’ll see an input volume slider and a real-time test bar that moves when Windows detects sound. This immediate visual feedback helps you verify that your microphone is working correctly without needing to open additional applications. Speak into your microphone and watch the blue bar respond to confirm it’s receiving audio input.
Configuring Input Audio Device Properties and Advanced Settings
Windows 11 offers detailed configuration options through the device properties page. To access these advanced settings:
Step 1: In the Sound settings Input section, click on the arrow next to your selected input device to expand the device options.
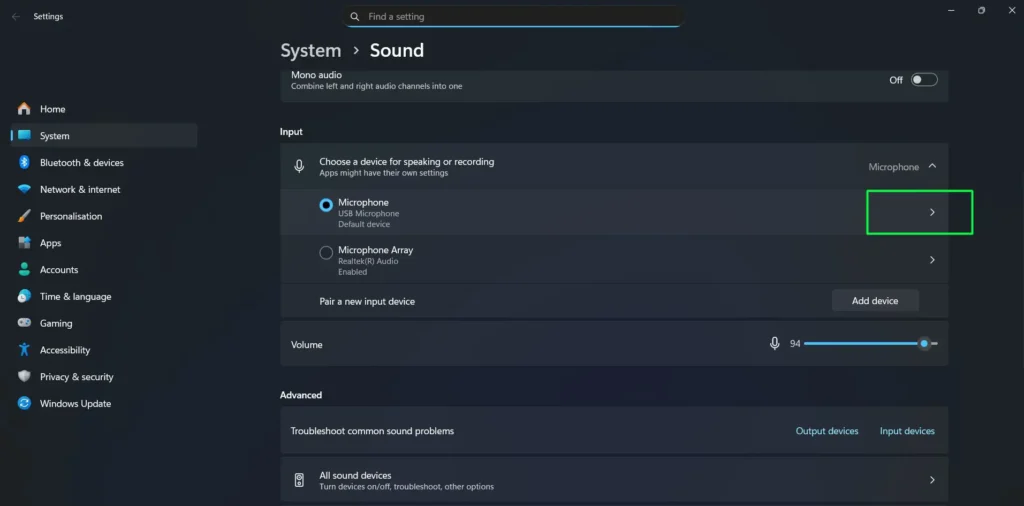
Step 2: The device properties page displays several important controls and information including the input volume slider, format selection, and additional settings.
Step 3: Use the Input volume slider to adjust your microphone’s sensitivity level. This slider controls how loud your microphone input appears to Windows and applications.
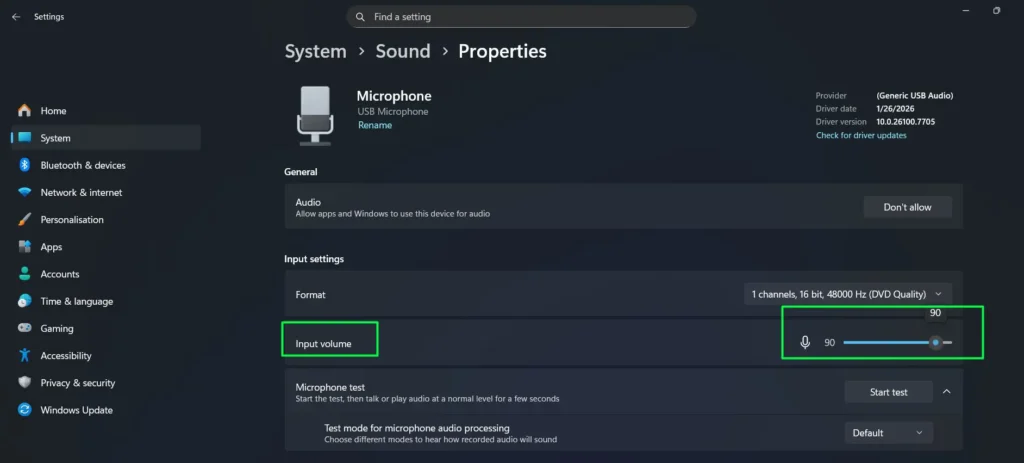
Step 4: Click “Start test” under the Test your microphone section to verify your microphone is capturing audio properly. Speak normally and watch the progress bar fill up to confirm proper functionality.
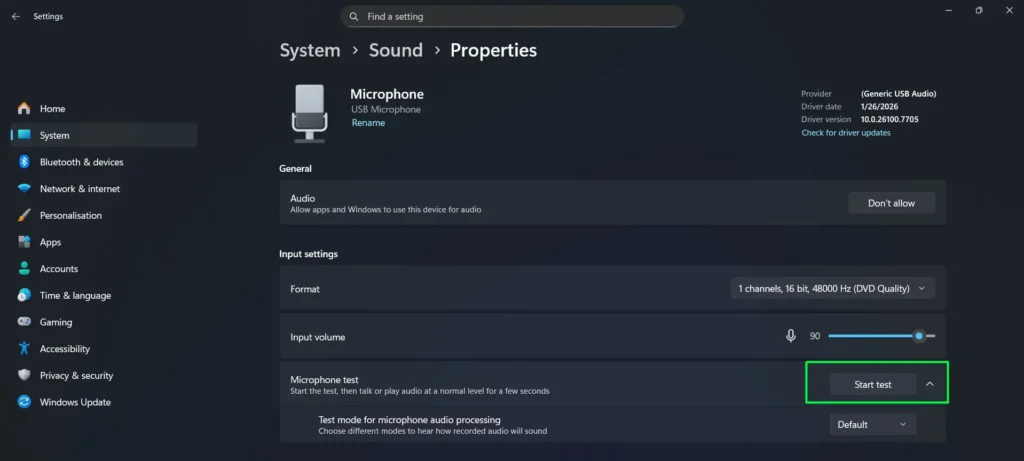
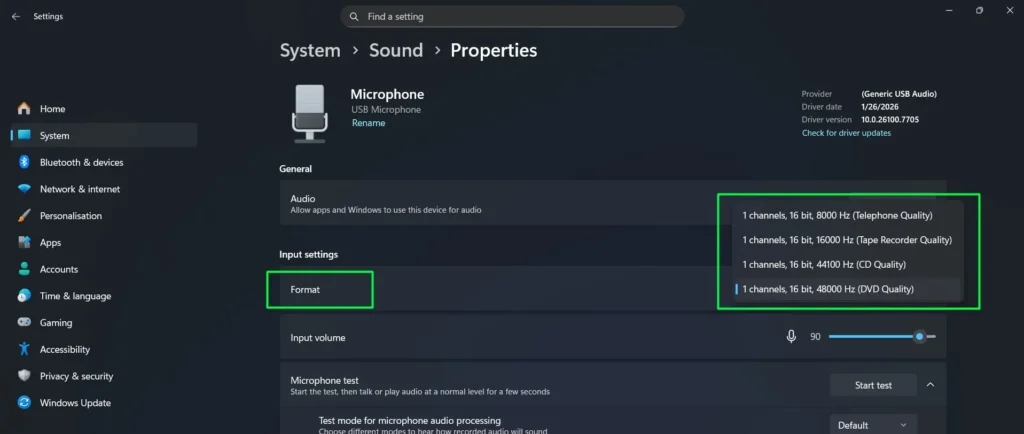
Step 5: Under the Format dropdown, select your preferred audio quality.
Options typically include “1 channel, 16 bit, 44100 Hz (CD Quality)” or “1 channel, 16 bit, 48000 Hz (DVD Quality)” for standard use, with higher quality options available for professional applications.
The device properties page also includes quick access to additional settings and troubleshooting tools. At the bottom of this page, you’ll find links to “More sound settings” which opens the classic Sound Control Panel for advanced configuration, and “Troubleshoot common sound problems” for automated problem resolution.
Accessing Advanced Properties Through Sound Control Panel
While Windows 11’s modern Settings interface handles most tasks, the classic Sound Control Panel provides additional advanced options. Access these settings through the following steps:
Step 1: Go to System > Sound in the Settings app, then scroll down and click “More sound settings” to open the classic Sound Control Panel.
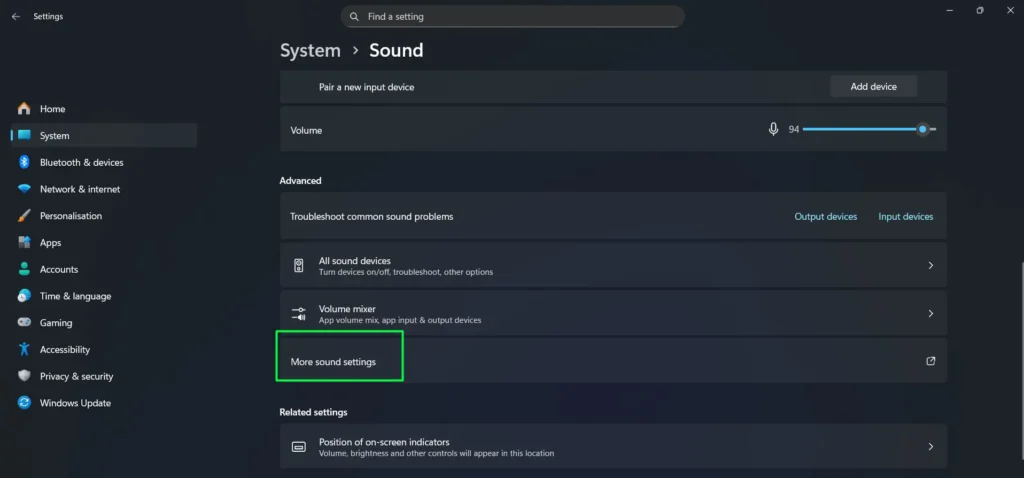
Step 2: In the Sound window, click the “Recording” tab to view all audio input devices.
Step 3: Locate your active microphone in the list — it will show a green checkmark and moving green bars when receiving audio.
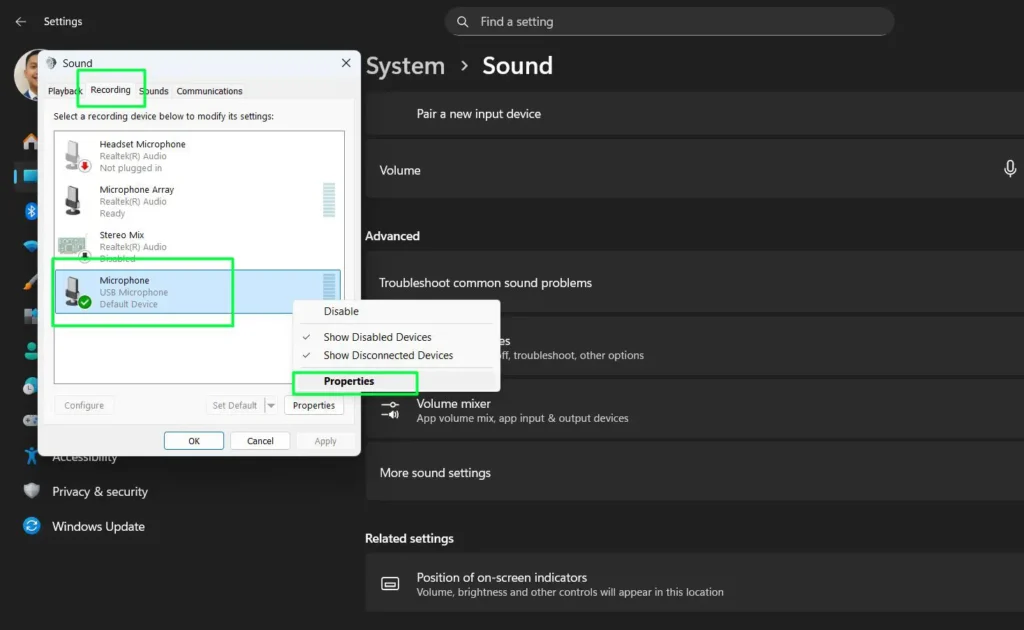
Step 4: Right-click your microphone and select “Properties.”
Step 5: Navigate through the tabs — General, Listen, Levels, Enhancements, and Advanced — for full configuration options.
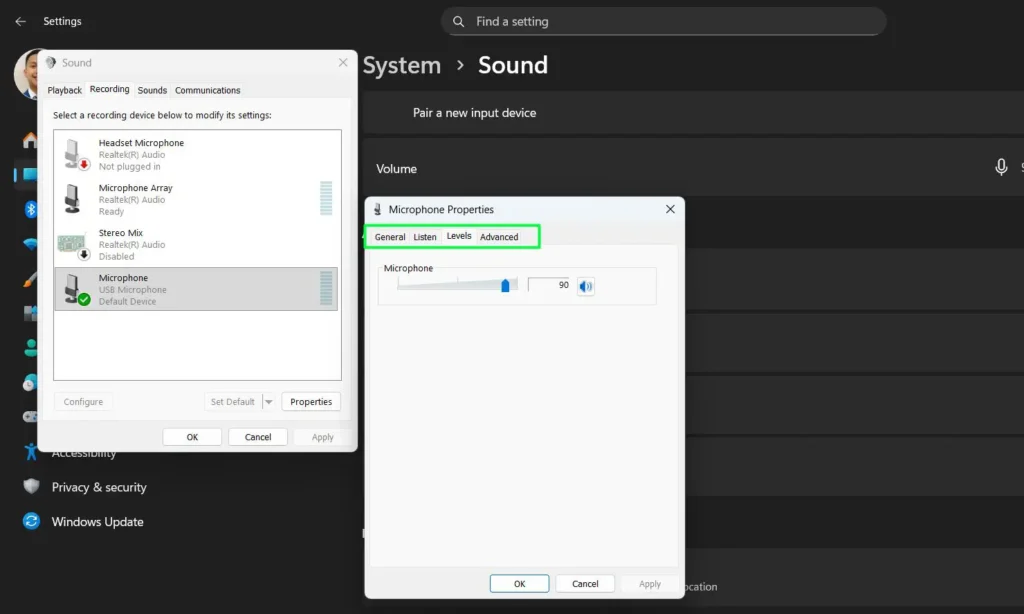
The General tab shows device info and lets you enable or disable the device. The Listen tab lets you hear your microphone through your speakers in real-time, though this can cause feedback. The Levels tab offers volume and boost controls with finer increments than the modern Settings interface.
Enabling Audio Enhancements
Windows 11 includes several audio enhancements that can improve audio quality through digital signal processing. Configure these enhancements through the following steps:
Step 1: Go to System > Sound, then scroll down and click “More sound settings.”

Step 2: In the Sound window, click the “Playback” tab, right-click your audio device, and select “Properties.”
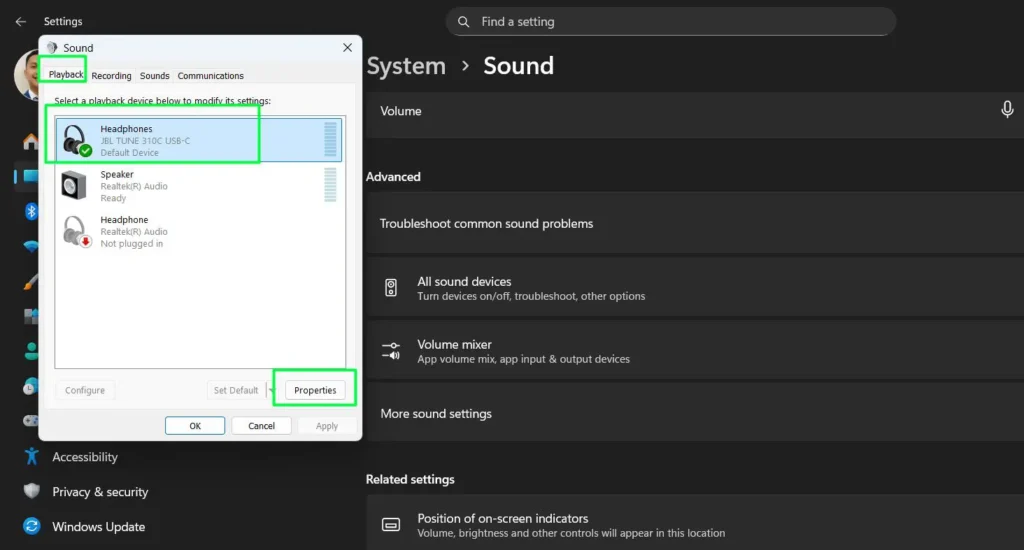
Step 3: In the Properties window, click the “Enhancements” tab to view available audio processing options.
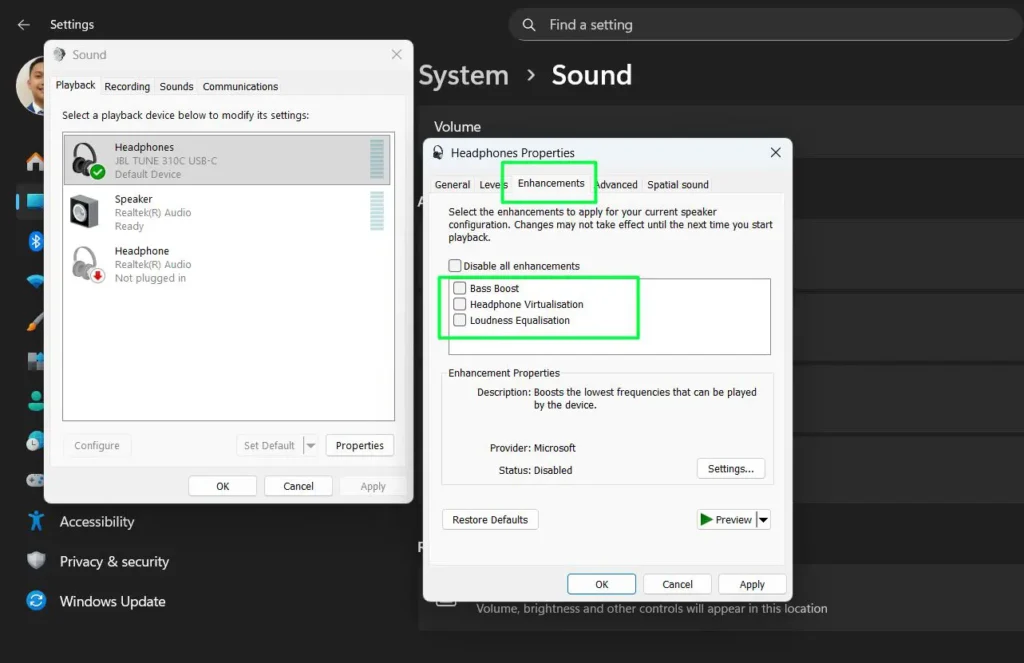
Step 4: Review the available enhancements, which may include:
- Bass Boost — Boosts the lowest frequencies that can be played by the device
- Headphone Virtualisation — Simulates a surround sound experience through headphones
- Loudness Equalisation — Balances volume levels for a more consistent listening experience
Step 5: Check the boxes next to the enhancements you want to enable, or check “Disable all enhancements” to use raw audio input.
Step 6: Click “Apply” to test the enhancements, then “OK” to save your settings.
Configuring Microphone Privacy and Permissions
Windows 11 includes comprehensive privacy controls for managing which applications can access your microphone. Configure these permissions through the following steps:
Step 1: Go to Settings and select Privacy & security
Step 2: scroll down to the App permissions section, and click “Microphone.”
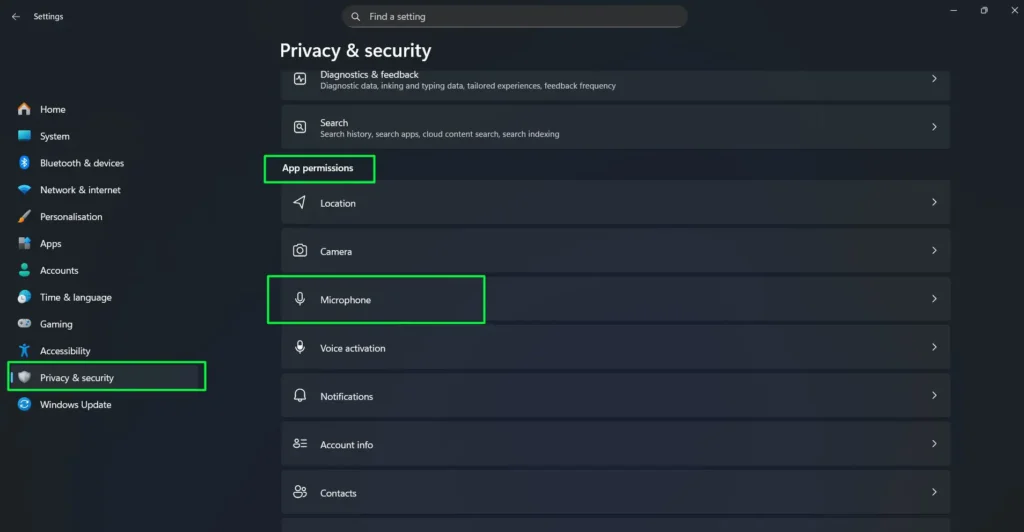
Step 3: At the top, ensure “Microphone access” is toggled On to allow any microphone functionality on your system.
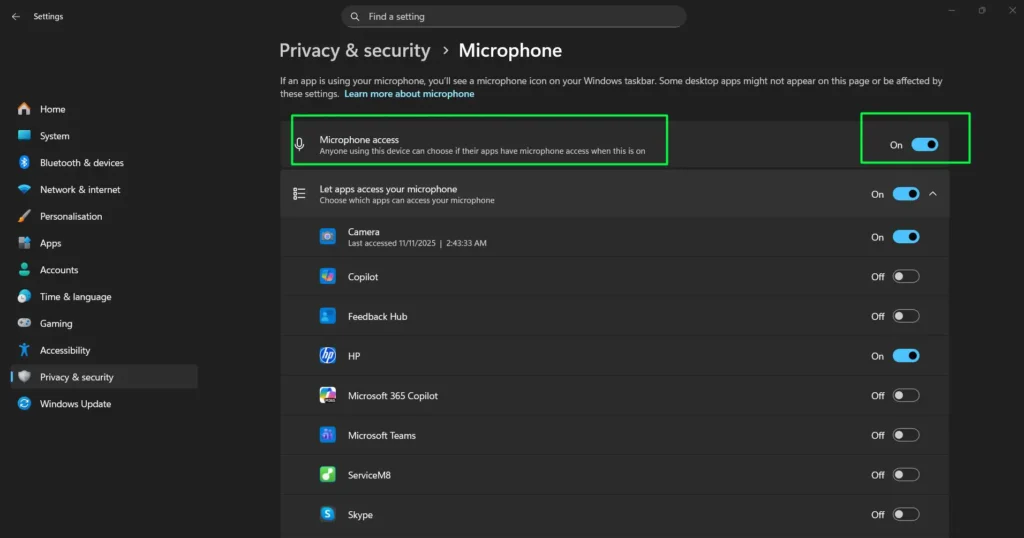
Step 4: Below that, enable “Let apps access your microphone” to allow Microsoft Store apps such as Camera, Copilot, Microsoft Teams, and Skype to use your microphone. Toggle individual apps On or Off based on your preferences.
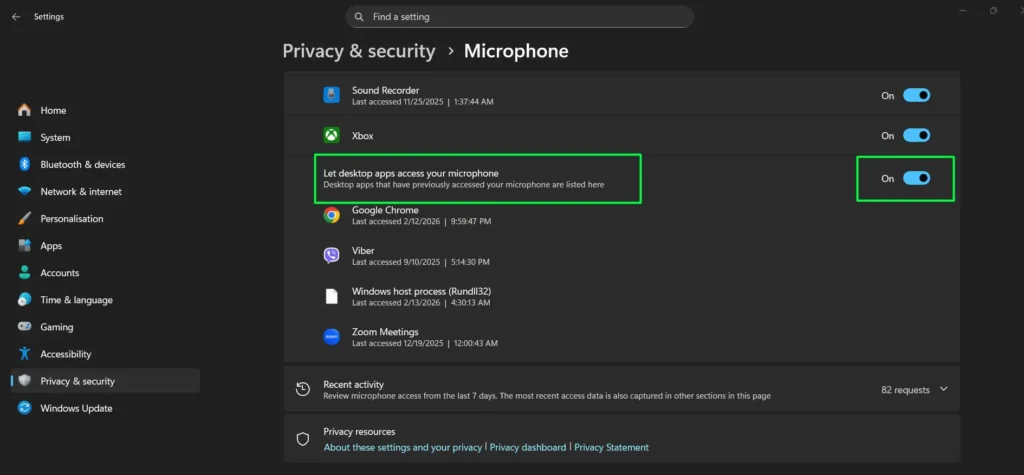
Step 5: Scroll down further and enable “Let desktop apps access your microphone” to allow traditional desktop applications such as Google Chrome, Viber, and Zoom Meetings to access your microphone.
Step 6: Review the Recent activity section, which shows microphone access requests from the last 7 days, helping you monitor which apps have been using your microphone.
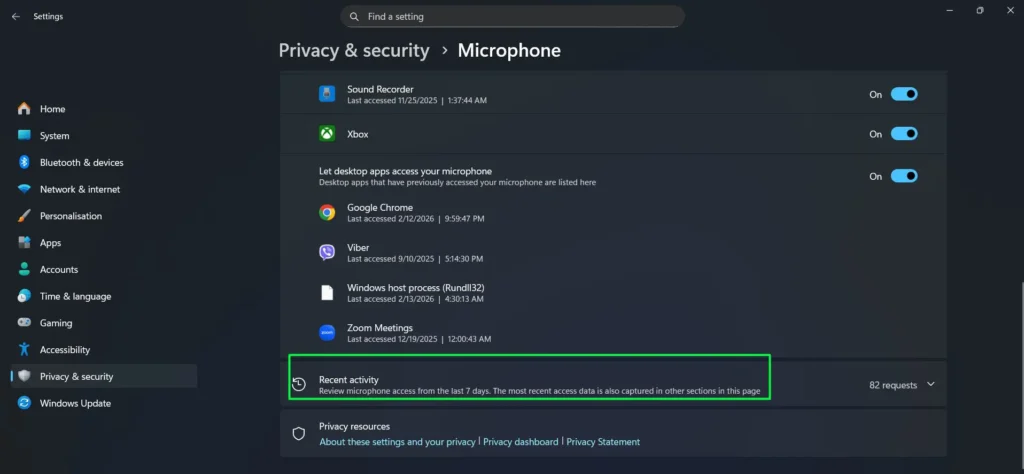
Step 7: Toggle individual application permissions On or Off based on your privacy preferences and which programs you trust with microphone access.
These privacy controls provide transparency and security for managing audio input access. You can prevent unwanted microphone usage while ensuring important applications like video conferencing tools and recording software continue to function properly.
Maintaining Optimal Input Device Performance
Regular maintenance ensures your audio input devices continue performing at their best. Keep the following tips and recommendations in mind:
Driver Updates
Check for driver updates monthly by visiting your microphone or audio interface manufacturer’s website. After major Windows 11 updates, always re-test your microphone configuration as updates can sometimes reset audio settings or require new drivers.
Physical Cleaning
Clean physical microphones regularly according to manufacturer guidelines. Use compressed air for grilles and gentle cleaning solutions for foam covers to prevent buildup that can muffle audio quality.
Settings Documentation
Document your optimal settings for each microphone — including volume levels, boost, format, and enhancements — so you can quickly restore them if a Windows update or system change resets your configuration.
Quality Monitoring
Create a monthly audio test recording using the same script to monitor for any gradual degradation in quality or sensitivity over time. Noticeable changes in required gain levels, increased background noise, or reduced clarity may indicate a hardware issue rather than a Windows configuration problem.
Cable and Connection Inspection
Inspect cables and connections quarterly for signs of wear, fraying, or corrosion, as physical damage is a common and often overlooked cause of audio quality issues.
Backup Devices
For critical applications such as streaming or professional recording, keep a backup microphone available to avoid unexpected downtime if your primary device fails.
Tips: Proper maintenance prevents gradual quality degradation and ensures your microphone continues delivering consistent, professional results. If issues persist despite good maintenance, consider professional repair or device replacement rather than further Windows configuration adjustments.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I fix microphone permissions in Windows 11?
Navigate to Settings > Privacy & security > Microphone and ensure all three main toggles are enabled: “Microphone access,” “Let apps access your microphone,” and “Let desktop apps access your microphone.” Scroll down to find the specific application having issues and verify its individual permission is turned on. If the toggles are grayed out, check if your organization has applied group policies that restrict microphone access. You may need administrator privileges to change these settings.
Why does my microphone sound muffled in Windows 11?
Muffled microphone audio typically results from incorrect sample rate settings or excessive enhancements. Open your microphone Properties from Sound settings, navigate to the Advanced tab, and try different default format options starting with 16-bit 48000 Hz. Disable all audio enhancements in the Enhancements tab by checking “Disable all enhancements.” Also verify that your physical microphone isn’t obstructed and that any foam covers are clean and properly positioned.
How can I reduce background noise on my microphone in Windows 11?
Enable noise suppression through your microphone’s Properties window in the Enhancements tab. Adjust your microphone levels to use minimal boost, as excessive boost amplifies background noise. Position your microphone closer to your mouth to improve the signal-to-noise ratio. For persistent noise issues, consider using third-party noise reduction software like Krisp or NVIDIA Broadcast, which offer more sophisticated processing than Windows 11’s built-in enhancements.
Can I use two microphones simultaneously in Windows 11?
Windows 11 allows only one default input device at a time for standard applications. However, you can use multiple microphones simultaneously with professional audio software or virtual audio cable applications like VoiceMeeter. These tools create virtual inputs that can combine signals from multiple physical microphones. Some professional audio interfaces also support multiple microphones through their control software, presenting them as separate channels to compatible recording applications.
Why is my USB microphone not showing up in Windows 11?
If your USB microphone isn’t detected, try connecting it to different USB ports, preferably USB 3.0 or higher directly on your motherboard rather than through a hub. Check Device Manager for any devices with warning symbols under “Audio inputs and outputs.” Update or reinstall drivers by right-clicking the device and selecting the appropriate option. Ensure the microphone works on another computer to rule out hardware failure. Some USB microphones require manufacturer-specific drivers downloaded from their website to function properly in Windows 11.
How do I set different microphones for different apps in Windows 11?
Windows 11 doesn’t provide native per-application input device assignment like it does for outputs. However, many applications include their own audio device selection in settings or preferences menus. Open each application’s audio settings and manually select the desired microphone. For more advanced control, use virtual audio cable software or application-specific routing tools that allow you to direct different microphones to different programs independently of Windows defaults.
What is the best audio format for my microphone in Windows 11?
For general use and video conferencing, 16-bit 44100 Hz or 48000 Hz provides excellent quality with minimal system resource usage. For professional recording, podcasting, and content creation, use 24-bit 48000 Hz or higher to capture more detail and provide flexibility during editing. Gaming and streaming typically work well with 16-bit 48000 Hz as it balances quality with performance. Select your format through the device properties page by clicking the Format dropdown and choosing the appropriate option for your needs.
How do I test if my microphone is working in Windows 11?
Navigate to Settings > System > Sound, scroll to Input, and select your microphone. Click the arrow to expand device properties, then click “Start test” under the Test your microphone section. Speak normally and watch the progress bar respond. Alternatively, open the Sound Control Panel, go to the Recording tab, and watch for green bars moving next to your microphone when you speak. You can also test using the Voice Recorder app by recording a short clip and playing it back.

