Knowing how to get help in Windows for sound and media playback issues is essential for maintaining an optimal audio experience. Whether you’re streaming your favorite tracks, watching concert recordings, or trying to enjoy high-quality audio content, sound problems can significantly impact your entertainment. This comprehensive guide provides expert solutions to help you navigate Windows’ built-in support tools, troubleshoot audio problems, and restore your system’s audio functionality.
Understanding Windows Sound and Media Architecture
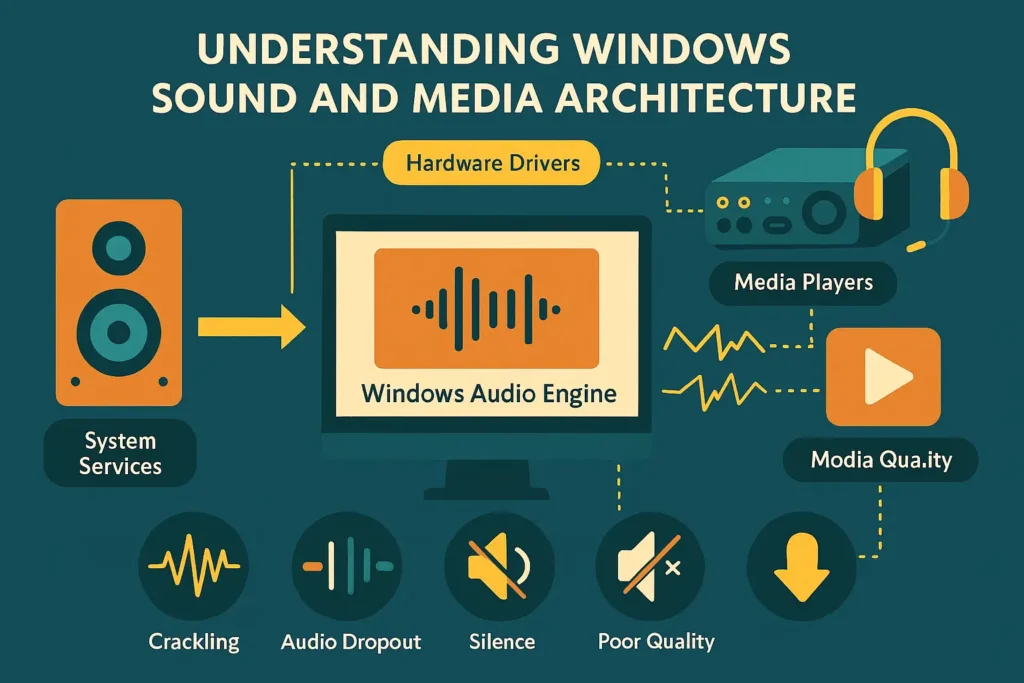
Windows audio systems involve multiple interconnected components: hardware drivers, system services, audio enhancements, and media players. When any component fails or conflicts with others, you’ll experience various symptoms including crackling sounds, audio dropouts, complete silence, or poor audio quality that affects your music enjoyment.
Modern Windows operating systems include sophisticated audio processing capabilities designed to enhance your listening experience. However, this complexity can sometimes create compatibility issues that require systematic troubleshooting approaches. Understanding these interactions helps you identify root causes and apply appropriate solutions more effectively.
The Windows Audio Engine manages audio streams, applies enhancements, and coordinates between applications and hardware. When problems occur, they often stem from conflicts within this complex system, making it crucial to understand where to find help and which tools to use.
Getting Started with Windows Built-in Help Tools
Accessing Windows Audio Troubleshooter
Windows includes a comprehensive audio troubleshooter that automatically detects and fixes common sound problems. Access this essential tool by right-clicking the speaker icon in your system tray and selecting “Troubleshoot sound problems.” The troubleshooter examines audio services, driver configurations, and system settings to identify issues systematically.
This automated diagnostic tool successfully resolves approximately 60-70% of basic audio problems, making it an excellent starting point for getting help. The troubleshooter checks audio device recognition, service status, default device assignments, and provides detailed explanations of discovered issues with recommended solutions.

For more advanced troubleshooting, access additional audio troubleshooters through Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Additional troubleshooters. Here you’ll find specialized tools for recording audio, playing audio, and resolving specific playback issues.
Using Windows Settings Audio Panel
Navigate to Settings > System > Sound to access Windows’ primary audio configuration interface. This panel provides comprehensive controls for managing audio devices, adjusting volume levels, configuring spatial audio, and accessing advanced sound settings.
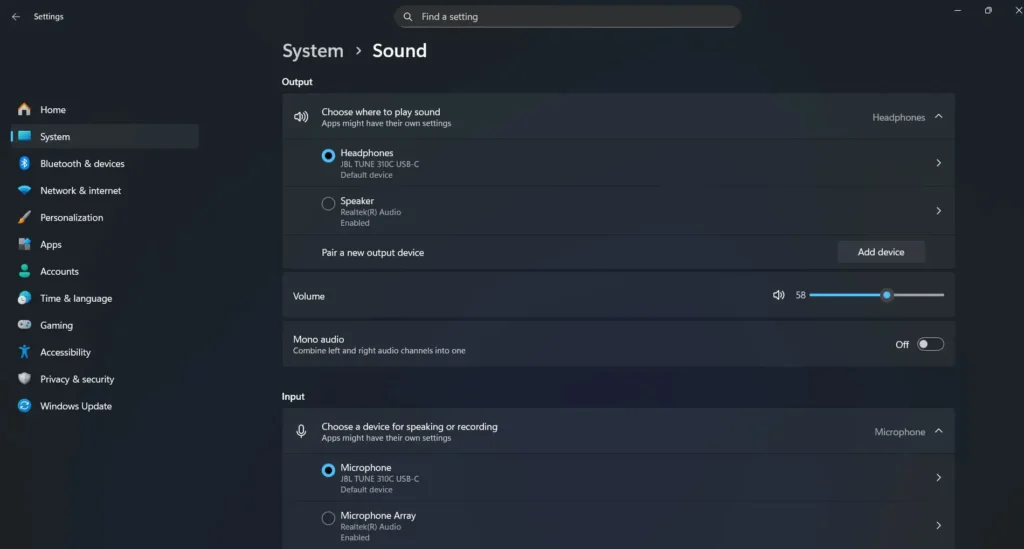
The Sound settings panel displays all available audio devices, allowing you to switch between different output sources easily. This proves particularly useful when troubleshooting issues with multiple audio devices or when optimizing settings for different types of music and songs.
Within advanced sound options, you can configure app volume and device preferences, enabling precise control over how different applications handle audio output. This granular control helps resolve conflicts between media players and system sounds.
Advanced Windows Audio Diagnostics
Device Manager Audio Troubleshooting
Device Manager serves as your primary tool for diagnosing hardware-related audio problems. Access it by pressing Windows + X and selecting “Device Manager.” Expand the “Sound, video and game controllers” section to examine your audio devices’ status and configuration.
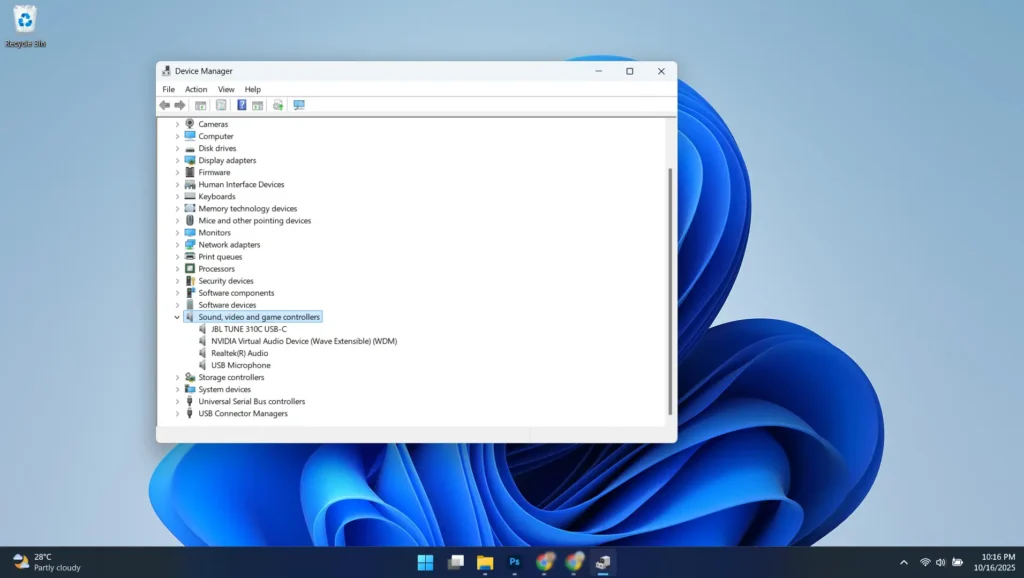
Look for devices displaying warning symbols such as yellow triangles or red X marks, which indicate driver problems requiring immediate attention. Right-click problematic devices to access properties, view error codes, and update or reinstall drivers as needed.
If your audio device doesn’t appear in Device Manager, this indicates fundamental hardware detection issues. Check physical connections, verify hardware compatibility, and ensure BIOS/UEFI settings haven’t disabled audio components.
Event Viewer Audio Error Analysis
Windows Event Viewer provides detailed logging information about system events, including audio-related errors and warnings. Access Event Viewer by typing “eventvwr” in the Start menu search box or through Administrative Tools.
Navigate to Windows Logs > System and Windows Logs > Application to review recent entries related to audio services and drivers. Look for error codes, warning messages, and timestamps that correspond to when audio problems occurred.
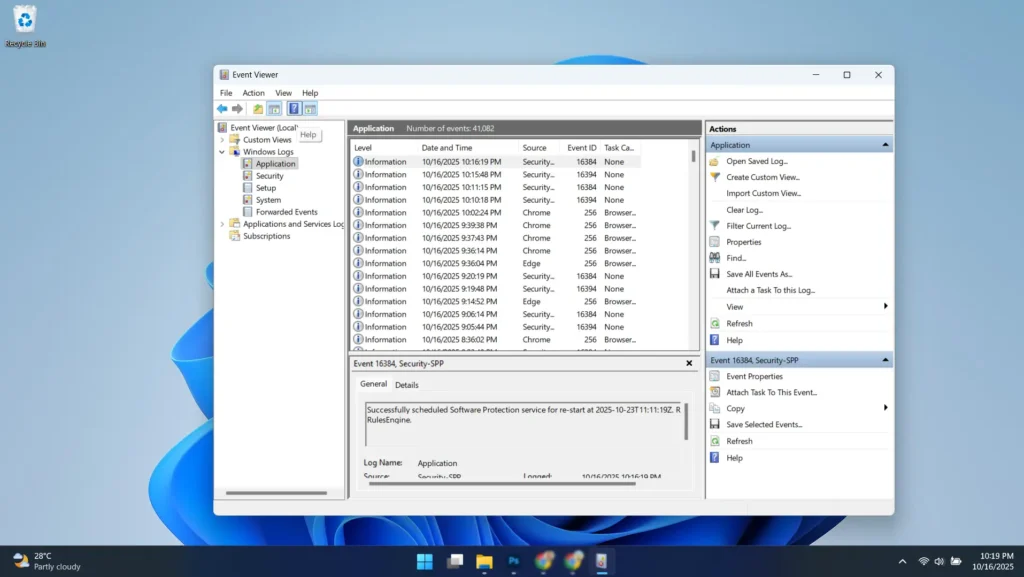
Event Viewer entries often provide specific error codes and module names that help identify the exact cause of audio failures. These details prove invaluable when researching solutions online or when contacting technical support for advanced assistance.
Audio Driver Management and Optimization
Identifying and Updating Audio Drivers
Proper audio driver management forms the foundation of stable Windows sound performance. Use System Information (msinfo32) to identify your exact audio hardware specifications, including manufacturer names, model numbers, and current driver versions.
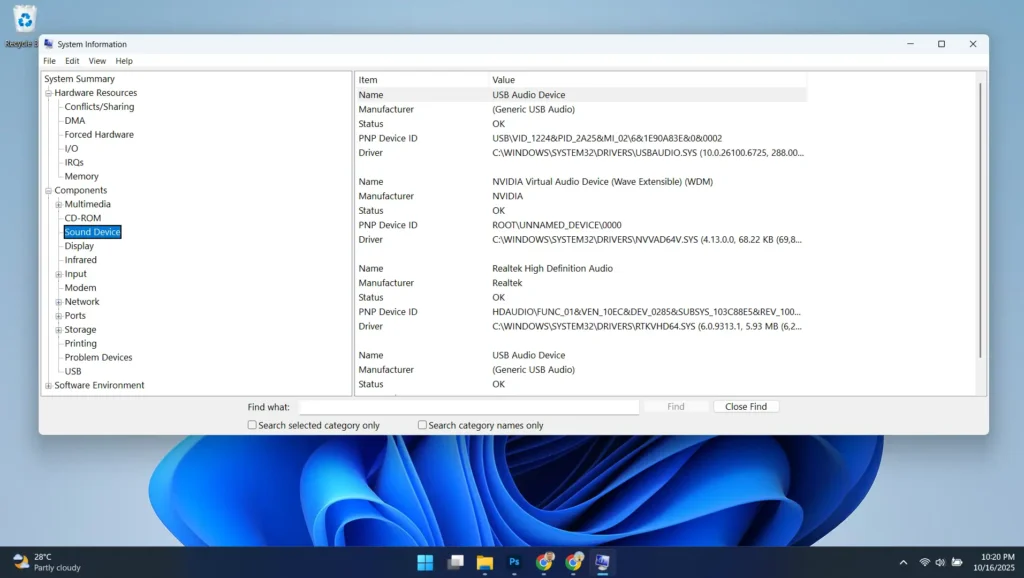
Visit your computer manufacturer’s support website or audio component manufacturer’s site to download current drivers. Major audio chip manufacturers like Realtek, Creative, and Intel regularly release updates that improve compatibility, add features, and enhance audio quality for music playback.
Before installing new drivers, completely uninstall existing versions using Device Manager or specialized uninstaller utilities. This clean installation approach prevents conflicts between old and new driver components that can cause ongoing audio problems.
Optimizing Audio Enhancements and Effects
Windows includes various audio enhancements designed to improve sound quality, but these features sometimes cause compatibility issues with certain hardware or applications. Access enhancement settings through Settings > System > Advanced >More Sound Settings > Playback devices > Properties > Enhancements.
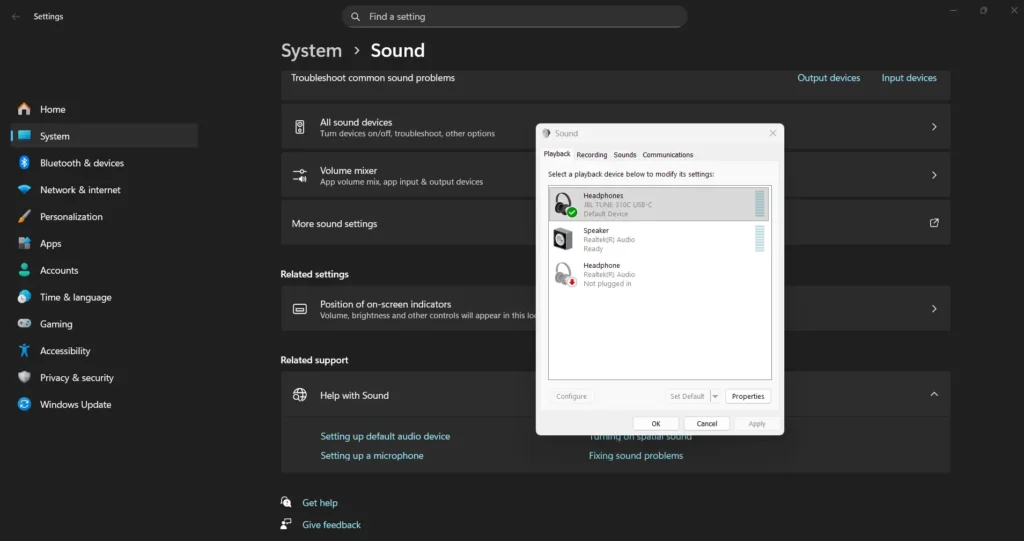
Common enhancements include bass boost, virtual surround, loudness equalization, and room correction. While these features can enhance your listening experience when using quality headphones, they may cause distortion or compatibility problems with some systems.
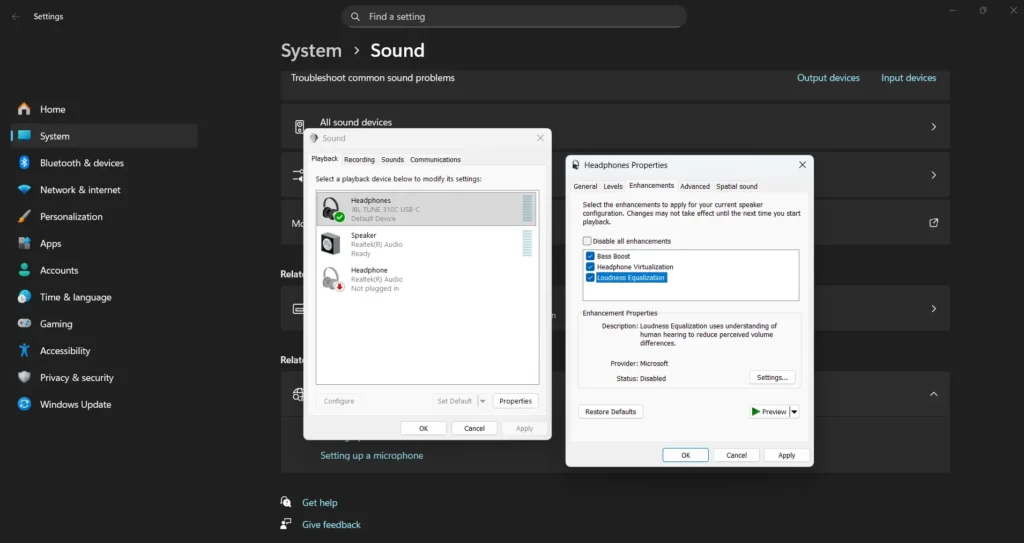
Disable all enhancements as a troubleshooting step if you experience audio quality issues. If problems resolve, re-enable enhancements individually to identify which specific feature causes conflicts with your system configuration.
Resolving Specific Playback Issues
Media Player Audio Problems
Different media players handle audio processing differently, which can lead to format compatibility issues or quality problems. Windows Media Player, VLC, and other applications each have unique audio processing pipelines that may conflict with system settings.
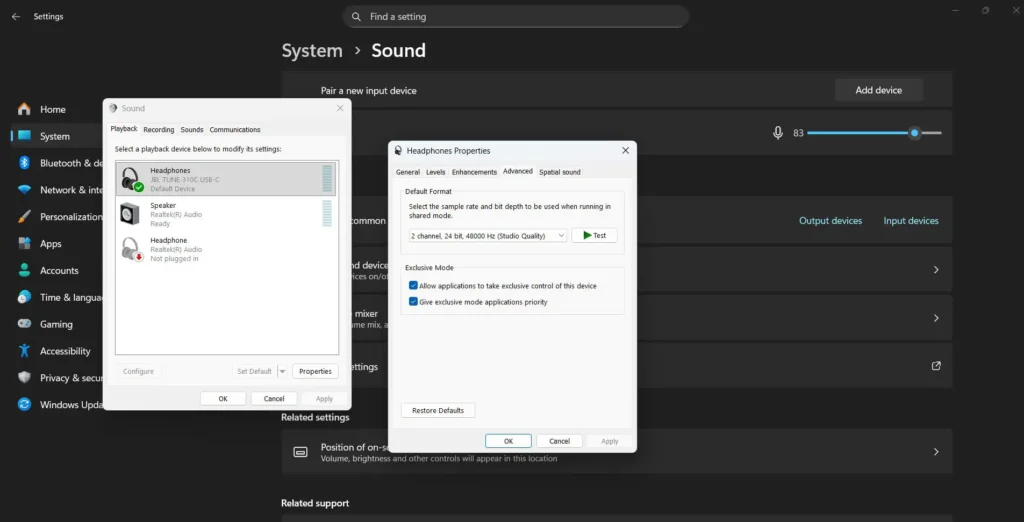
Configure exclusive mode settings in Sound Control Panel to allow applications direct hardware access, bypassing Windows audio processing. This approach often resolves quality issues and reduces audio latency for critical listening applications.
For users evaluating different audio equipment and comparing earbuds, ensuring proper media player configuration becomes crucial for accurate sound evaluation and enjoyment.
Streaming Service Audio Quality
Streaming platforms like Spotify, Apple Music, and YouTube Music each implement different audio processing methods that may not integrate optimally with Windows audio systems. Check application-specific audio settings to ensure maximum quality output.
Many streaming services offer high-quality audio options that require specific driver capabilities and system configurations. Verify your audio drivers support the sample rates and bit depths required for lossless audio streaming.
Configure Windows to use the highest quality audio format supported by your hardware through Settings > System > Advanced >More Sound Settings > Playback devices > Properties > Advanced. Match these settings with your streaming service’s quality preferences for optimal results.
Professional Audio System Configuration
ASIO Driver Implementation
Professional audio applications often require ASIO (Audio Stream Input/Output) drivers for low-latency performance and high-quality audio processing. These specialized drivers bypass Windows’ standard audio architecture for direct hardware communication.
Install manufacturer-provided ASIO drivers for professional audio interfaces, or use generic ASIO4ALL drivers for consumer hardware. ASIO configuration requires careful buffer size adjustment to balance latency and stability based on your system’s capabilities.
ASIO drivers prove essential for music production, professional audio editing, and critical listening applications where timing accuracy and audio quality take priority over general system compatibility.
Multi-Channel and Surround Sound Setup
Configuring multi-channel audio systems requires precise speaker positioning and careful Windows configuration. Access Speaker Setup through Settings > System > Advanced >More Sound Settings > Playback devices > Properties > Advanced to configure your specific speaker arrangement.
Test each channel individually using Windows’ built-in speaker test function to verify proper signal routing and speaker connections. Incorrect channel mapping can significantly impact your audio experience and make troubleshooting more difficult.
Calibrate speaker distances and levels using Windows’ built-in tools or third-party calibration software to achieve optimal sound balance and imaging for your listening environment.
Network and Streaming Audio Troubleshooting
Wi-Fi Audio Streaming Issues
Wireless audio streaming depends heavily on network stability and bandwidth availability. Audio dropouts and quality issues often result from network congestion, interference, or insufficient bandwidth rather than Windows audio system problems.
Monitor network performance using Windows’ built-in network diagnostics and third-party tools to identify connectivity issues. Prioritize audio traffic using Quality of Service (QoS) settings in your router configuration to ensure consistent streaming performance.
Position wireless devices away from interference sources like microwaves, baby monitors, and other 2.4GHz devices that can disrupt audio streaming connections and cause intermittent playback problems.
Bluetooth Audio Optimization
Bluetooth audio requires specific codec support and proper pairing configuration for optimal performance. Windows supports various Bluetooth audio codecs including SBC, aptX, and AAC, each offering different quality and latency characteristics.
Update Bluetooth drivers regularly and verify codec compatibility between your Windows system and audio devices. Some high-quality Bluetooth codecs require specific driver versions and may not work with generic Windows Bluetooth stacks.
Ready to fix Bluetooth connectivity issues? Visit this comprehensive guide to learn How to Reinstall Bluetooth Driver: Complete Guide and restore your wireless audio connections with expert step-by-step instructions.
Manage Bluetooth device power settings to prevent automatic disconnection during extended listening sessions. Configure advanced power management options to maintain consistent audio connections without sacrificing battery life on portable devices.
System Performance and Audio Quality
Resource Management for Audio Applications
Audio processing requires consistent system resources and can suffer when other applications consume excessive CPU, memory, or storage bandwidth. Monitor system performance using Task Manager and Resource Monitor during audio playback to identify resource conflicts.

Close unnecessary background applications and disable non-essential startup programs to free system resources for audio processing. Configure Windows power management settings to prevent CPU throttling during audio playback sessions.
Optimize storage performance by defragmenting hard drives and ensuring adequate free space for audio caching and temporary file operations that support smooth playback performance.
Real-Time Audio Processing Optimization
Configure Windows for real-time audio processing by adjusting thread priorities and system responsiveness settings. Access these advanced options through System Properties > Advanced > Performance Settings > Advanced.
Disable Windows Search indexing for audio file directories to prevent storage access conflicts during playback. Configure antivirus software to exclude audio directories from real-time scanning to avoid playback interruptions.
Optimize virtual memory settings to provide adequate swap space for audio processing while minimizing disk access that can cause audio dropouts during intensive playback sessions.
Third-Party Audio Tools and Utilities
Audio Analysis and Diagnostic Software
Specialized audio diagnostic tools provide detailed analysis capabilities beyond Windows’ built-in troubleshooting options. Tools like Audio Precision’s APx software suite, REW (Room EQ Wizard), and LatencyMon help identify specific audio system problems.
These professional tools measure audio quality parameters including frequency response, distortion levels, and timing accuracy that help pinpoint hardware or configuration issues affecting your listening experience.
Use audio test signals and measurement tools to objectively evaluate your system’s performance and verify that troubleshooting efforts actually improve audio quality rather than just masking underlying problems.
Driver and System Maintenance Utilities
Third-party driver management utilities like Driver Booster, Snappy Driver Installer, or manufacturer-specific tools help maintain current driver versions and identify compatibility issues before they cause audio problems.
System cleaning utilities remove temporary files, registry errors, and conflicting configurations that can accumulate over time and affect audio system stability and performance.
Regular system maintenance using these tools helps prevent audio issues from developing and ensures optimal performance for your Windows audio configuration.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is my Windows audio crackling or distorted?
Audio crackling typically results from driver conflicts, incorrect sample rate settings, or system resource limitations. Start by updating your audio drivers, checking for Windows updates, and adjusting audio quality settings in Sound Control Panel. Disable audio enhancements temporarily to determine if they’re causing the distortion.
How do I fix no sound coming from my Windows computer?
First, check that your audio device is set as the default playbook device in Sound settings. Run the Windows audio troubleshooter, verify driver installation in Device Manager, and ensure the volume isn’t muted or set too low. Check physical connections and try different audio output devices to isolate the problem.
What should I do when Windows doesn’t recognize my audio device?
Restart your computer to refresh hardware detection, then check Device Manager for any devices with warning symbols. Try uninstalling and reinstalling audio drivers, checking for Windows updates, and verifying that the device works on another computer. BIOS/UEFI settings may also need adjustment for certain audio hardware.
How can I improve audio quality for music playback in Windows?
Configure your audio device to use the highest supported sample rate and bit depth in Sound Control Panel. Disable unnecessary audio enhancements that may color the sound, use high-quality media players, and ensure your audio drivers are current. Consider using exclusive mode for critical listening applications.
Why does my Bluetooth audio keep disconnecting in Windows?
Bluetooth audio disconnections often result from power management settings, driver issues, or interference. Update your Bluetooth drivers, adjust power management settings to prevent automatic device sleep, and check for interference from other wireless devices. Maintain proximity between devices and ensure adequate battery levels.

