Audio settings play a crucial role in determining how you experience music, movies, podcasts, and any digital content. Whether you’re using premium headphones, budget earbuds, or high-end speakers, understanding and optimizing your audio settings can transform your listening experience from mediocre to extraordinary. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about configuring audio settings across different devices and platforms to achieve the best possible sound quality.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Audio Settings

Audio settings encompass various parameters that control how sound is processed, transmitted, and reproduced through your audio devices. These settings affect everything from volume levels and frequency response to spatial audio and noise cancellation features. The key components include sample rate, bit depth, audio format, equalizer settings, and device-specific enhancements.
Sample rate determines how many times per second your audio is sampled, typically measured in kilohertz (kHz). Higher sample rates like 48 kHz or 96 kHz can provide better audio quality, especially for high-resolution music files. Bit depth, measured in bits, affects the dynamic range and overall fidelity of your audio. Most modern systems support 16-bit or 24-bit audio, with the latter offering superior quality for audiophiles and professional applications.
Audio formats also play a significant role in your listening experience. Lossless formats like FLAC and ALAC preserve all original audio data, while compressed formats like MP3 and AAC reduce file sizes at the cost of some audio quality. Understanding these fundamentals helps you make informed decisions when configuring your audio settings for optimal performance.
Optimizing Audio Settings on Windows Systems
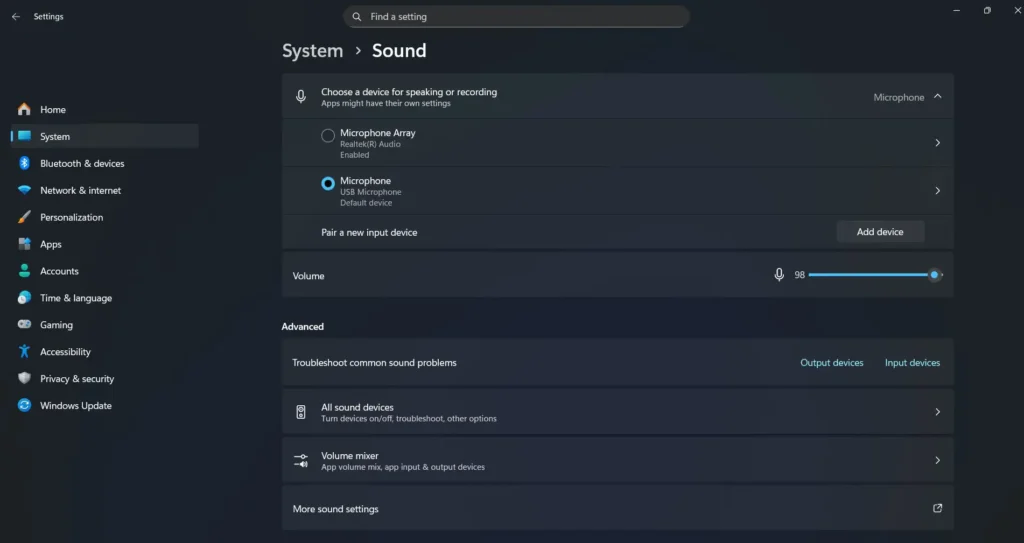
Windows offers extensive audio configuration options through its Sound Control Panel and Settings app. To access advanced audio settings, right-click the speaker icon in your system tray and select “Open Sound settings.” From here, you can choose your default playback and recording devices, adjust volume levels, and access device properties for detailed configuration.
For enhanced audio quality, navigate to the device properties and explore the Advanced tab. Here you can select higher sample rates and bit depths, enable audio enhancements, and configure exclusive mode settings. Exclusive mode allows applications to take complete control of your audio device, potentially improving sound quality by bypassing Windows’ audio processing.
Windows also includes spatial audio features like Windows Sonic and Dolby Atmos support. These technologies create immersive three-dimensional soundscapes that enhance gaming, movie watching, and music listening experiences. Enable these features through the Spatial audio dropdown in your device properties to experience more engaging audio content.
macOS Audio Configuration Best Practices
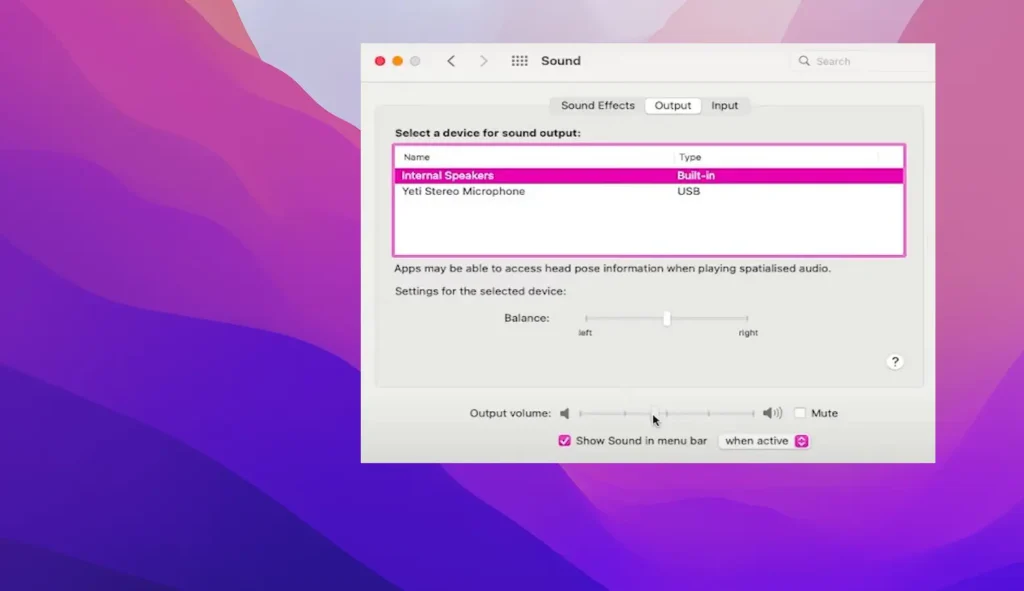
Apple’s macOS provides sophisticated audio management through the Audio MIDI Setup utility and System Preferences. Access Audio MIDI Setup by pressing Command+Space and typing “Audio MIDI Setup” to configure advanced audio parameters. This utility allows you to set sample rates, create aggregate devices, and configure multi-output setups for professional audio workflows.
The built-in equalizer in Music app (formerly iTunes) offers preset audio profiles for different music genres and listening preferences. Experiment with these presets or create custom equalizer settings to match your personal taste and the characteristics of your audio equipment. The “Late Night” setting, for example, reduces dynamic range for comfortable listening in quiet environments.
For users with high-end audio equipment, consider exploring the audio quality settings within the Music app preferences. Access these through Music > Preferences > Playback to configure streaming and import quality settings that work best with your audio setup and internet connection speed.
Mobile Device Audio Optimization
Smartphone audio settings have evolved significantly, offering features that rival desktop systems. On iOS devices, navigate to Settings > Music to configure audio quality preferences for different connection types and explore options for optimizing playback based on your listening environment and data usage preferences.
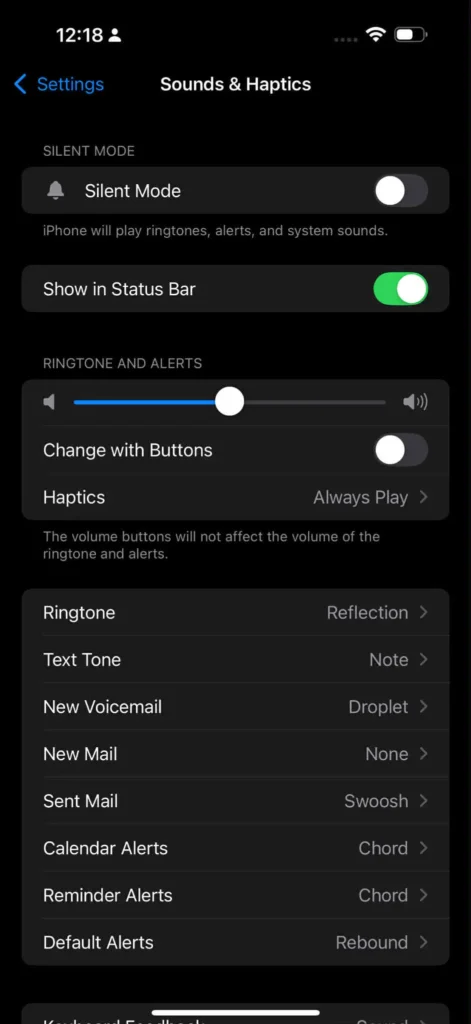
The iOS Control Center provides quick access to spatial audio controls when using compatible AirPods or Beats headphones. Swipe down from the top-right corner of your screen and long-press the volume slider to access spatial audio toggles and head tracking features that create immersive listening experiences for supported content.
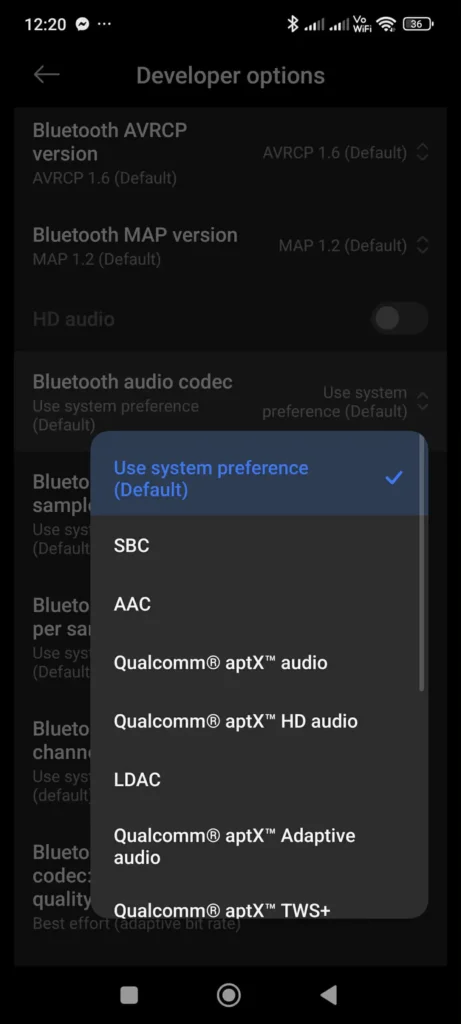
Android devices offer even more granular control through developer options and third-party applications. Enable Developer Options by tapping the build number seven times in About Phone, then navigate to the Bluetooth audio codec settings. Here you can select high-quality codecs like LDAC, aptX HD, or AAC for wireless audio transmission that maintains excellent sound quality.
Many Android manufacturers include custom audio enhancement features. Samsung’s Adapt Sound technology, for instance, personalizes audio settings based on your hearing profile, while Sony’s DSEE HX upscaling improves compressed audio quality. Explore your device’s sound settings to discover manufacturer-specific features that can enhance your listening experience.
Streaming Service Audio Settings
Popular streaming platforms offer various audio quality settings that significantly impact your listening experience. Spotify Premium subscribers can enable “Very High” quality streaming at 320 kbps, while the free tier is limited to 160 kbps. Access these settings through Spotify’s preferences menu and consider enabling high-quality streaming only on Wi-Fi to preserve mobile data.
Apple Music provides lossless and high-resolution audio options that deliver studio-quality sound. Navigate to Settings > Music > Audio Quality to configure lossless streaming preferences for different connection types. Keep in mind that lossless audio requires compatible hardware and consumes significantly more bandwidth and storage space than standard compressed audio.
Tidal offers multiple audio quality tiers, including CD-quality lossless and Master Quality Authenticated (MQA) files. These high-resolution formats showcase the full dynamic range and detail of original recordings, making them ideal for critical listening sessions with high-quality audio equipment. When comparing different streaming platforms and their audio quality offerings, consider your listening habits and equipment capabilities.
Gaming Audio Configuration
Gaming audio settings require special consideration for competitive gameplay and immersive experiences. Most games offer separate volume controls for music, sound effects, and voice chat, allowing you to balance these elements according to your preferences. Competitive gamers often reduce music volume while emphasizing sound effects to better hear footsteps and environmental cues.
Enable surround sound or spatial audio features in games that support them. Technologies like Dolby Atmos, DTS:X, and proprietary gaming audio solutions create three-dimensional soundscapes that enhance immersion and provide competitive advantages through accurate positional audio. Configure these settings in both your game preferences and system audio settings for optimal results.
Consider investing in gaming-specific audio equipment with customizable profiles. Many gaming headsets include software that allows you to create custom equalizer settings, virtual surround sound configurations, and microphone adjustments. Popular brands offer companion applications with preset profiles optimized for different game genres and listening preferences.
Professional Audio Settings and DAW Configuration
Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs) require precise audio configuration for professional music production and recording. Set your audio interface to appropriate sample rates and buffer sizes that balance audio quality with system performance. Lower buffer sizes reduce latency but require more processing power, while higher buffer sizes provide stable performance with increased delay.
Configure your DAW’s audio preferences to match your hardware capabilities and project requirements. Most professional projects use 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz sample rates with 24-bit depth, providing excellent quality while maintaining manageable file sizes. Higher sample rates like 96 kHz or 192 kHz are reserved for specialized applications that require extreme fidelity.
Monitor your CPU usage and adjust buffer sizes accordingly during recording and mixing sessions. Enable direct monitoring on your audio interface to eliminate latency during recording, and use hardware monitoring features to create custom headphone mixes for performers during recording sessions.
Troubleshooting Common Audio Issues
Audio problems often stem from incorrect settings, driver issues, or hardware conflicts. When experiencing audio dropouts, crackling, or distortion, start by checking your sample rate settings across all applications and ensuring they match your hardware capabilities. Mismatched sample rates can cause audio artifacts and compatibility issues.
Update your audio drivers regularly to maintain optimal performance and compatibility with new software and operating system updates. Manufacturer websites typically provide the latest drivers optimized for your specific audio hardware. Consider rolling back to previous driver versions if new updates introduce stability issues or performance degradation.
Disable unnecessary audio enhancements and effects that may interfere with audio playback. While these features can improve certain types of content, they may cause issues with high-quality audio files or specific applications. Test your audio with enhancements disabled to isolate potential causes of audio problems.
Hardware Considerations for Optimal Audio Settings
Your choice of audio hardware significantly impacts the effectiveness of various audio settings. High-impedance headphones may require dedicated amplification to reach their full potential, while sensitive in-ear monitors might benefit from impedance adapters to reduce noise and improve channel balance. When comparing different headphone options, consider how various models respond to equalizer adjustments and audio enhancements.
Audio interfaces provide superior digital-to-analog conversion compared to built-in computer sound cards, enabling you to take full advantage of high-resolution audio settings. Look for interfaces with low noise floors, high dynamic range, and support for the sample rates and bit depths you plan to use. Professional interfaces often include additional features like hardware monitoring, multiple outputs, and MIDI connectivity.
Consider the acoustic environment when configuring audio settings for speakers. Room acoustics significantly affect how audio settings translate to your listening experience. Use acoustic treatment, proper speaker positioning, and room correction software to optimize your listening environment and make the most of your audio configuration efforts.
Advanced Audio Settings and Future Technologies
Emerging audio technologies continue to expand the possibilities for audio customization and enhancement. Object-based audio formats like Dolby Atmos and DTS:X represent the future of immersive audio, providing content creators with unprecedented control over spatial audio placement and movement. These technologies require compatible hardware and content but offer revolutionary listening experiences when properly configured.
Artificial intelligence is increasingly being integrated into audio processing, offering personalized equalizer settings, automatic noise reduction, and content-aware audio enhancement. Companies like Sony, Bose, and Apple are developing AI-powered audio features that adapt to your listening habits and environment automatically.
Binaural audio and head-related transfer function (HRTF) personalization represent cutting-edge developments in spatial audio. These technologies create highly realistic three-dimensional audio experiences by modeling how sound waves interact with your individual ear shape and head geometry. As these technologies become more accessible, they will likely become standard features in consumer audio devices.
Frequently Asked Questions
What sample rate should I use for everyday listening?
For most listeners, 44.1 kHz or 48 kHz sample rates provide excellent audio quality that’s indistinguishable from higher rates in normal listening conditions. These rates work well with all types of earbuds and headphones while maintaining reasonable file sizes and system resource usage. Higher sample rates like 96 kHz or 192 kHz are primarily beneficial for professional audio production and may not provide audible improvements for casual listening.
How do I know if my audio settings are optimized?
Optimal audio settings depend on your specific hardware, listening preferences, and content types. Start with manufacturer recommendations for your audio devices, then make gradual adjustments while listening to familiar, high-quality content. Pay attention to clarity, balance, and comfort during extended listening sessions. If audio sounds natural and engaging without fatigue, your settings are likely well-optimized.
Should I use audio enhancements and equalizers?
Audio enhancements can improve certain aspects of your listening experience but should be used judiciously. Start with flat, neutral settings and make small adjustments based on your preferences and content. Some enhancements like virtual surround sound can be beneficial for gaming and movies, while others like bass boost might color the audio in undesirable ways. Trust your ears and disable any enhancement that makes audio sound unnatural or fatiguing.
What’s the difference between exclusive mode and shared mode audio?
Exclusive mode allows applications to take complete control of your audio device, potentially providing better sound quality by bypassing system audio processing and mixing. Shared mode allows multiple applications to play audio simultaneously through system mixing. Use exclusive mode for critical listening or professional applications, but stick with shared mode for general computer use where you need multiple audio sources.
How often should I update my audio drivers?
Update audio drivers when you experience problems, install new audio software, or update your operating system. While newer drivers often provide improvements and bug fixes, they can occasionally introduce new issues. Keep a backup of working drivers and be prepared to roll back if new drivers cause problems. Check manufacturer websites quarterly for driver updates, but only install them if you’re experiencing issues or need new features.

